前回はSELinuxのコマンドについて説明しました。
今回は実際にSELinuxの設定を行ってみたいと思います。
この記事ではコマンドの内容については説明しないので、コマンドについては前回の記事を確認してください。
この記事で行うこと
1. 今回の例の状況説明
以下の記事にてWordPressのインストール時の設定としてSELinuxの設定を行っています。
このSELinux設定を行わず、またブール値の httpd_can_network_connect を off とします。( httpd_can_network_connect はCentOS8のデフォルトでは on となっていますが、説明のため off に設定しました)
さて、この状態でインストールしたWordPressのサイトに行くと以下の画像のようにアクセス出来ません。
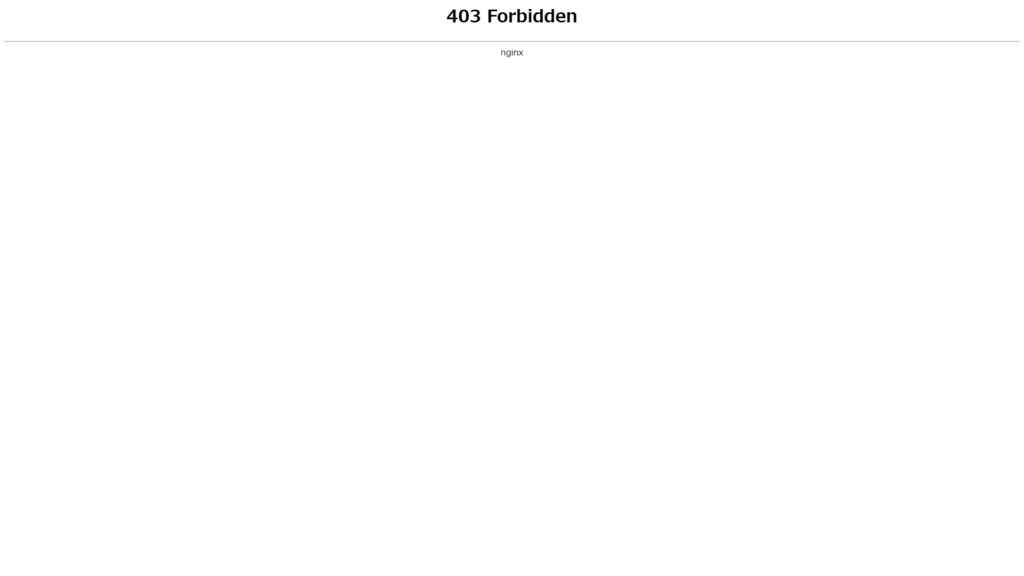
この問題を解決していきます。
2. SELinuxのモード変更
まず最初に、SELinuxをPermissive(許容)モードに変更します。
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0これでSELinuxにて本来ブロックされるべき挙動もログに記録するだけで許容されるようになります。
この状態でもう一度アクセスしてみると、問題なく画面が表示されるようになることを確認します。
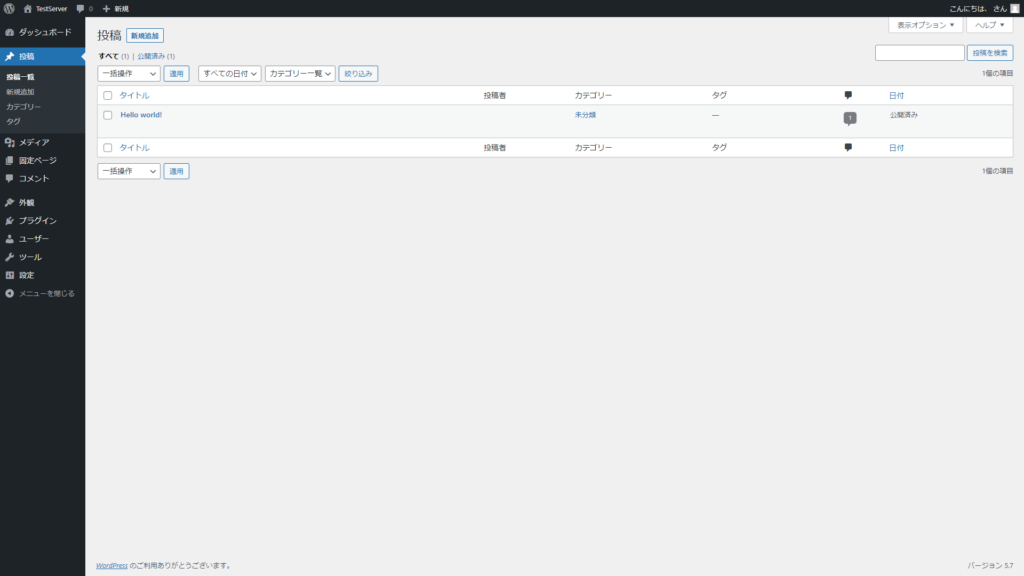
もしモードをPermissiveにしても問題が解決しない場合は原因はSELinuxだけではない(或いはSELinuxは関係ない)ので、他の原因を探します。
3. ログの確認
SELinuxをPermissiveにしているのは実質SELinuxを無効化しているのと変わりありません。
このため、SELinuxの問題となる設定を直して再度Enforcing(有効)に戻す必要があります。
問題となっている設定を見つけるためにまずログを確認します。
[root@localhost ~]# journalctl --since today --identifier setroubleshootすると、アクセスした時間帯に以下のような警告が続いているのが確認出来ます。
N月 XX HH:MM:SS localhost setroubleshoot[269700]: failed to retrieve rpm info for /srv/wordpress/index.php
N月 XX HH:MM:SS localhost setroubleshoot[269700]: SELinux is preventing /usr/sbin/php-fpm from getattr access on the file /srv/wordpress/index.php. For complete SELinux messages run: sealert -l 7b752501-4529-4e22-bcc0-fa406a5dc8c3
N月 XX HH:MM:SS localhost setroubleshoot[269700]: SELinux is preventing /usr/sbin/php-fpm from getattr access on the file /srv/wordpress/index.php.
***** Plugin catchall_labels (83.8 confidence) suggests *******************
If you want to allow php-fpm to have getattr access on the index.php file
Then you need to change the label on /srv/wordpress/index.php
Do
# semanage fcontext -a -t FILE_TYPE '/srv/wordpress/index.php'
where FILE_TYPE is one of the following: NetworkManager_exec_t, NetworkManager_log_t, NetworkManager_tmp_t, abrt_dump_oops_exec_t, abrt_etc_t, abrt_exec_t, abrt_handle_event_exec_t, abrt_helper_exec_t, (以下コンテキストタイプの名称が続く
Then execute:
restorecon -v '/srv/wordpress/index.php'
***** Plugin catchall (17.1 confidence) suggests **************************
If you believe that php-fpm should be allowed getattr access on the index.php file by default.
Then you should report this as a bug.
You can generate a local policy module to allow this access.
Do
allow this access for now by executing:
# ausearch -c 'php-fpm' --raw | audit2allow -M my-phpfpm
# semodule -X 300 -i my-phpfpm.pp
このログにはSELinuxでブロックされた事と、解決案が載っています。
今回は2つの解決策があるようです。
読んでみると、上の方(確度が83.8%の方)はファイルのコンテキストを変更するというもの、下の方(確度が17.1%の方)はポリシーモジュールを作成するという要するにファイルとコンテキストのルールを変更しろというものです。
前々回の記事で基本的にはファイルのコンテキストを変更することで対応するとも言ったことですし今回はその通りに対応を行います。
問題はどのコンテキストに変更するのかという点です。
今回はWebサーバに関連するものなので、httpdから始まるものを探してみますが、それでも何個か見つかります。
次に考えられるのは既に存在するコンテキストのルールに似たようなものが無いかです。
以下のコマンドでhttpdを含むファイルコンテキストを付与するルールを探します。
[root@localhost ~]# semanage fcontext -l | grep httpd | more最後の | more は一行ずつ表示するためのコマンドです。Enterキーで次の行、Spaceキーで次のページに進めることが出来ます。
こうして見ると、丁度WordPress用のものと思しきルールが見つかりました。
/usr/share/wordpress/.*\.php regular file system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_script_exec_t:s0
/usr/share/wordpress/wp-content/upgrade(/.*)? all files system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_rw_content_t:s0
/usr/share/wordpress/wp-content/uploads(/.*)? all files system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_rw_content_t:s0
/usr/share/wordpress/wp-includes/.*\.php regular file system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_script_exec_t:s0実はWordPressの記事で解説していたSELinuxの設定は若干雑なもので、httpd_unified のブール値を有効化することで、とりあえずWeb関連のファイルコンテキストであれば細かいコンテキストは関係なく読み書き可能にしていました。
WordPressに関してはこのコンテキスト設定を流用すれば httpd_unified 無しでも機能しそうです。
4. 設定の変更
先ほど調べたコンテキストを設定してみます。
[root@localhost ~]# semanage fcontext --add --type httpd_sys_script_exec_t "/srv/wordpress/.*\.php"
[root@localhost ~]# semanage fcontext --add --type httpd_sys_rw_content_t "/srv/wordpress/wp-content/uploads(/.*)?"
[root@localhost ~]# semanage fcontext --add --type httpd_sys_rw_content_t "/srv/wordpress/wp-content/upgrade(/.*)?"
[root@localhost ~]# semanage fcontext --add --type httpd_sys_script_exec_t "/srv/wordpress/wp-includes/.*\.php"設定したら、実際のファイルに反映しましょう。
[root@localhost ~]# restorecon -R /srv/wordpress/5. 設定の確認と設定追加
設定が終わったらSELinuxのモードをEnforcingに戻してアクセスをしてみます。
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 1しかし、Enforceingに戻すとまたブロックされることが分かります。
再度ログを確認すると、また別のファイルがブロックされていることが分かります。
N月 XX HH:MM:SS localhost setroubleshoot[270725]: SELinux is preventing /usr/sbin/php-fpm from read access on the file twentytwenty-ja.mo. For complete SELinux messages run: sealert -l d4edf941-d042-4d57-88d3-c57e2243fabb
N月 XX HH:MM:SS localhost setroubleshoot[270725]: SELinux is preventing /usr/sbin/php-fpm from read access on the file twentytwenty-ja.mo.
***** Plugin catchall_labels (83.8 confidence) suggests *******************
If you want to allow php-fpm to have read access on the twentytwenty-ja.mo file
Then you need to change the label on twentytwenty-ja.mo
Do
# semanage fcontext -a -t FILE_TYPE 'twentytwenty-ja.mo'
where FILE_TYPE is one of the following: NetworkManager_exec_t, NetworkManager_tmp_t, abrt_dump_oops_exec_t, abrt_etc_t, abrt_exec_t, abrt_handle_event_exec_t, abrt_helper_exec_t, abrt_retrace_coredump_exec_t, (以下コンテキストタイプの名称が続く
Then execute:
restorecon -v 'twentytwenty-ja.mo'
***** Plugin catchall (17.1 confidence) suggests **************************
If you believe that php-fpm should be allowed read access on the twentytwenty-ja.mo file by default.
Then you should report this as a bug.
You can generate a local policy module to allow this access.
Do
allow this access for now by executing:
# ausearch -c 'php-fpm' --raw | audit2allow -M my-phpfpm
# semodule -X 300 -i my-phpfpm.pp
今回流用した設定は /usr/share/wordpress/ のものなので、もしかしたらより上層に設定されているルールがあるかもしれません。
という事で以下のコマンドで順に遡って探してみます。
[root@localhost ~]# semanage fcontext -l | grep /usr/share | more
[root@localhost ~]# semanage fcontext -l | grep /usr | moreすると、以下の行が見つかりました。
/usr/.* all files system_u:object_r:usr_t:s0どうやら /usr/ 以下のファイルには usr_t タイプがつくようです。
では、これも設定に追加します。
[root@localhost ~]# semanage fcontext --add --type usr_t "/srv/wordpress/.*"
[root@localhost ~]# restorecon -R /srv/wordpress/設定後に再度接続してみると問題なく表示されるはずです。
6. ブール値の問題
しかし、プラグインを追加しようとすると、またもや問題が発生します。
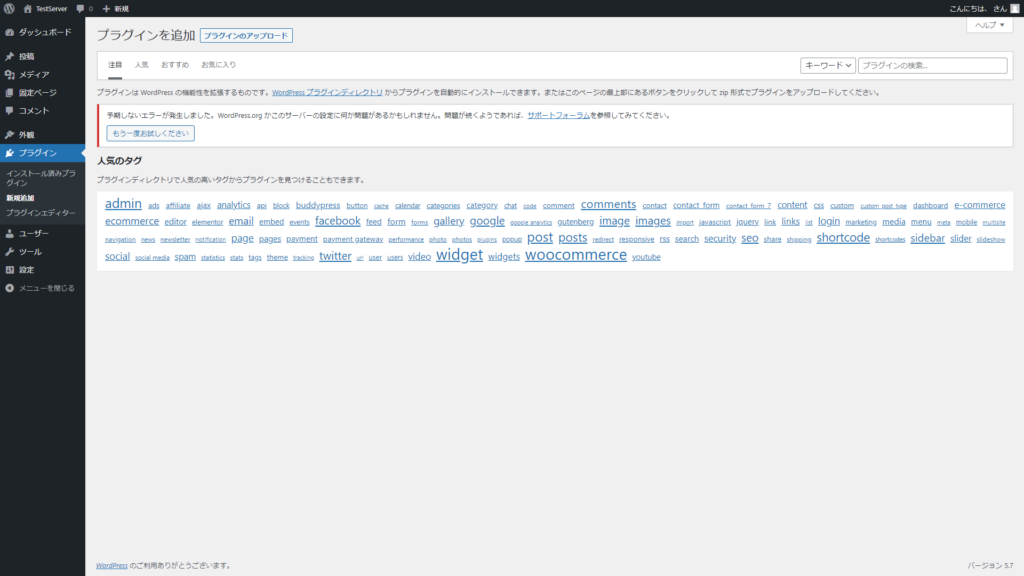
まずはもう一度SELinuxを許容モードにして問題が解決することを確認します。
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0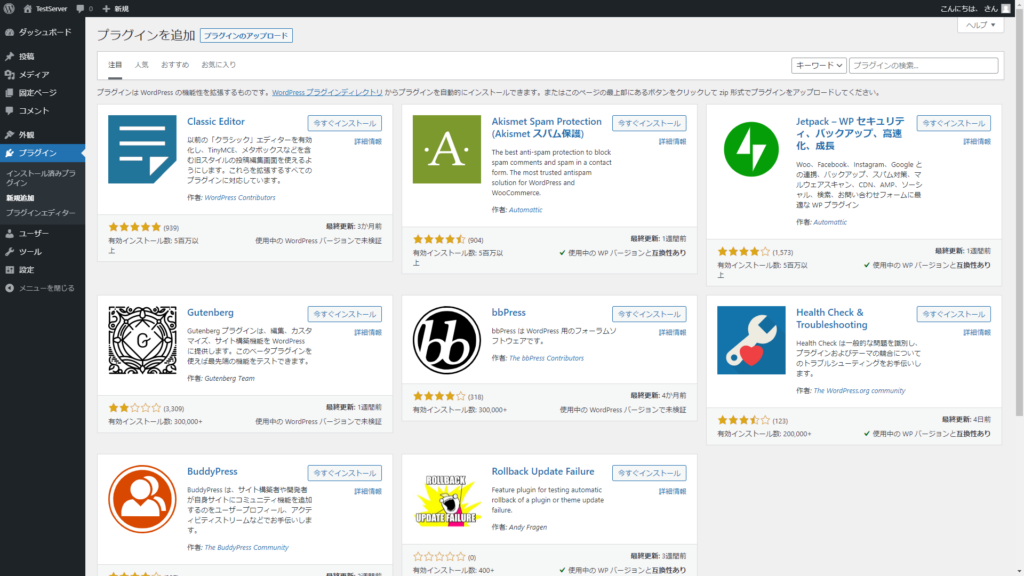
どうやらこれもSELinuxの問題のようです。
これもまたログを見てみます。
[root@localhost ~]# journalctl --since today --identifier setroubleshootすると、以下のようなログが見つかります。
N月 XX HH:MM:SS localhost setroubleshoot[5744]: SELinux is preventing /usr/sbin/php-fpm from name_connect access on the tcp_socket port 443. For complete SELinux messages run: sealert -l be4342ca-4eb7-4c68-81d7-3ded567fdcc9
N月 XX HH:MM:SS localhost setroubleshoot[5744]: SELinux is preventing /usr/sbin/php-fpm from name_connect access on the tcp_socket port 443.
***** Plugin catchall_boolean (24.7 confidence) suggests ******************
If you want to allow httpd to can network connect
Then you must tell SELinux about this by enabling the 'httpd_can_network_connect' boolean.
Do
setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect 1
***** Plugin catchall_boolean (24.7 confidence) suggests ******************
If you want to allow httpd to graceful shutdown
Then you must tell SELinux about this by enabling the 'httpd_graceful_shutdown' boolean.
Do
setsebool -P httpd_graceful_shutdown 1
***** Plugin catchall_boolean (24.7 confidence) suggests ******************
If you want to allow httpd to can network relay
Then you must tell SELinux about this by enabling the 'httpd_can_network_relay' boolean.
Do
setsebool -P httpd_can_network_relay 1
***** Plugin catchall_boolean (24.7 confidence) suggests ******************
If you want to allow nis to enabled
Then you must tell SELinux about this by enabling the 'nis_enabled' boolean.
Do
setsebool -P nis_enabled 1
***** Plugin catchall (3.53 confidence) suggests **************************
If you believe that php-fpm should be allowed name_connect access on the port 443 tcp_socket by default.
Then you should report this as a bug.
You can generate a local policy module to allow this access.
Do
allow this access for now by executing:
# ausearch -c 'php-fpm' --raw | audit2allow -M my-phpfpm
# semodule -X 300 -i my-phpfpm.pp
1番下の新規ルールを作成するという解決策を除いて、ブール値の変更が提示されています。
今回はWordPressがインターネット上のプラグインを探しに行けるようにしたい、つまりWebサーバがネットワークに接続出来れば良いので、1番上の解決策を取ります。
書かれてあるとおりにブール値を変更するコマンドを実行します。
[root@localhost ~]# setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect 1その後またSELinuxを有効に戻します。
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 1この状態でアクセスしても問題なくプラグインの一覧が見えるはずです。
これで、WordPressのSELinux設定が完了となります。
まとめ
今回はWordPressを例にSELinuxの設定を行ってみました。
ただ、今回の方法は最適な設定というよりも大きく間違った設定をしないというものになります。
厳密に設定を行おうとするとSELinuxのコンテキストの許可設定を確認するためのツールをインストールして確認しつつ設定を探るというものになります。
しかし多少設定が甘くても「よく分からないけど動かないから切る」よりかはマシなので、ぜひ設定するようにしてください。
それなりに規模のあるソフトウェアだとSELinuxの設定例を出している場合もあるので、そういった情報も活用してみてください。